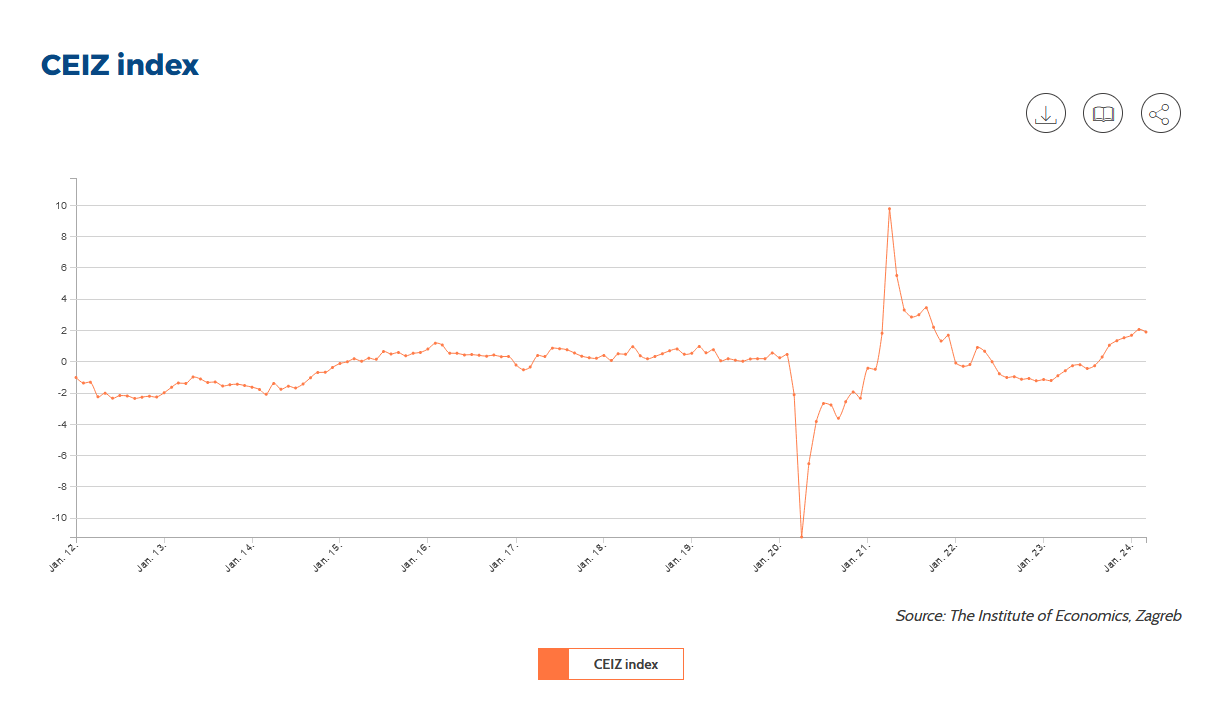
The Importance of the CEIZ Index
The Coincident Economic Index of the Institute of Economics, Zagreb (CEIZ)[1] is a composite coincidence index, which is an index that tracks how well different indicators – specifically macroeconomic and fiscal indicators: inflation, wages, unemployment, etc. align with each other over time. In this regard, the CEIZ index is applied for the Croatian economy, using monthly macroeconomic, fiscal, and demographic data and statistical methodologies such as correlation analysis, logit model, and Markov transition model. The indicator aims to measure the current state of the business cycle, substituting the shortcomings of the GDP data and their timing publication. This approach offers obvious advantages, including the ability to track the business cycle in real-time and to predict its future movements. Among the main problems are the complexity of selecting the most appropriate components, from the data of the respective countries where it is going to be implemented. The results show that this indicator accurately reflects GDP fluctuations, making it a useful tool for economic analysis.
In the context of Kosovo, this index could be implemented despite some limitations regarding the quality of public data. Its publication would provide objective and unbiased information regarding economic developments and would serve policymakers for necessary interventions and corrective measures, as well as a more qualitative debate. As the first step to implementing the index, one needs to understand the types of data that must be used, where in this case are public data from institutions. Below, the aspect of the current situation regarding public data in Kosovo is addressed, since they are the initial and main element in the creation of the index.
Current Status regarding Public Data in Kosovo
This analysis aims to review the current state of publicly available data in Kosovo, with a particular focus on the analysis of indices related to the economic performance of various sectors, including industry, consumption, and construction.
One of the key indicators examined is the Producer Price Index (PPI)[2], which reflects price changes in Kosovo’s industrial sectors. The PPI index is divided into several subcategories such as for total prices of industrial products, for energy and for products such as machinery, consumer durables and products of the mining, quarrying, and manufacturing sectors. The initial constituting data provide a detailed view of the performance and price trends in industrial sectors and can help in monitoring price stability and long-term economic planning. Another important indicator that has been examined is the Consumer Price Index (CPI)[3], which provides data on changes in the prices of goods and services that consumers use every day. The CPI includes subcategories for prices of goods, transport, food, beverages, and tobacco, as well as other categories related to housing, and health care. About other economic sectors, construction data have also been examined, where the Construction Cost Index and the Construction Materials Price Index[4] are important indicators to monitor construction activity and developments in this sector. It must be noted that some industrial indexes and construction data, require a higher level of disaggregation, thus potentially making their extraction difficult.
Another important aspect that has been addressed is the analysis of employment and wage indicators in different sectors. Data on gross and net wages of employees, provided by the Tax Administration of Kosovo (TAK)[5], provide an important insight into the distribution of income and help assess the employment situation and economic inequality. In terms of international trade, data on exports and imports are rich, including information on various goods such as food, beverages, chemicals, machinery, and industrial products.
From the observation it shows that there are data available for various sectors, such as agriculture, manufacturing, wages, and financial services, but some categories are still unavailable, thus making it important to address their shortcomings.
Background of the Analysis
Benet Maloku, researcher with an interest in open data and digitalization, currently, at the Riinvest Institute since 2022, used the POLICY ANSWERS fellowship between 9 and 20 December 2024 at the Economic Institute of Zagreb (EIZ) to deepen his understanding of the methodology used in the creation of the CEIZ index, a key economic tool developed by the institute. The fellowship provided an opportunity to explore the process behind constructing the index, focusing on its underlying data and the calculation steps involved.
Initially, the activities centred on acquiring the constituent data for the CEIZ index. This data, which is publicly available through various government institutions, forms the foundation of the index and plays a crucial role in its accuracy and relevance. Under the expert guidance of Marina Tkalec, a senior research associate at EIZ, Benet had the opportunity to explore and analyse this data in detail. She provided invaluable insights into the selection, interpretation, and validation of the data, offering a deeper understanding of the methodology employed by the institute. After familiarising himself with the data, he actively participated in the process of calculating the CEIZ index. This hands-on experience allowed him to apply the steps involved in processing and analysing the data, ultimately contributing to the generation of the final output of the CEIZ index. Throughout this process, he gained a broader understanding of how each component of the data influences the overall index score.
In addition to working on the CEIZ index, he was fortunate to participate in various informative sessions hosted by EIZ. These sessions provided an overview of ongoing projects and research initiatives at the institute, enriching his experience and enhancing his knowledge of the broader scope of the work undertaken. By participating in activities, he was able to better understand how both institutes, Riinvest and EIZ, approach research and use this experience to better the approaches in the development of economic policies.
Conclusions and Outlook
The Riinvest Institute has begun work to create the conditions for replicating this index. By implementing this index, a more accurate and comprehensive picture of Kosovo’s business cycle could be shown. Finally, the analysis highlighted that, although there is a range of indicators and data for different sectors of the economy, some gaps in public data are present. Addressing data gaps and strengthening capacities for their collection and reporting is an important step toward improving the analysis and forecasting of economic dynamics.
[1] CEIZ index.https://www.eizg.hr/indices-351/ceiz-index/352. Accessed 27 January 2025.
[2] Producer Price Index (PPI), Q3 2024. https://askapi.rks-gov.net/Custom/190e21e4-6eb4-4a8d-8d80-719bf1f1573e.pdf. Accessed 27 January 2025.
[3] Harmonized Index of Consumer Prices. https://askapi.rks-gov.net/Custom/329cdf3e-b9f7-4b90-a6c9-63731657d745.pdf. Accessed 27 January 2025.
[4] Construction Cost Index. https://askapi.rks-gov.net/Custom/5d6fd7f3-ff28-46a7-842b-bf8b45f48dd2.pdf. Accessed 27 January 2025.
[5] Tax Administration of Kosovo, Open Data. https://www.atk-ks.org/en/open-data/. Accessed 27 January 2025.